

Digvijay Singh
Nov 06, 2022
6 min read
Copy link
For an early-stage application selecting a DB is still a tricky part. And the selection lies between a SQL DB(MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc..) or a NoSQL DB(MongoDB, Cassandra, etc..). Both options have Pros and Cons in their way.
SQL databases offer a separate layer of security and management systems to manage the data and structure them in the most meaningful manner. We can't deny the fact that this requires some expertise in SQL, its terminology and methodology. It may also require separate resources to accomplish this.
On the other hand, MongoDB, a NoSQL database doesn't require the SQL language and its methodology for maintaining the database system. So, have a basic knowledge of databases and you are good to go.
MongoDB is a viable solution if you choose Node.js and some libraries for backend development and require fast data extraction as it stores data in the form of JSON documents which is highly efficient to parse and manipulate in a Javascript environment. And the integration of MongoDB with Node.Js is also an ease process. Just a few lines of code and your database will be up and running. You will require these two libraries mongoose and mongodb
MongoDB is a viable solution if you choose Node.js and some libraries for backend development and require fast data extraction as it stores data in the form of JSON documents which is highly efficient to parse and manipulate in a Javascript environment. And the integration of MongoDB with Node.Js is also an ease process. Just a few lines of code and your database will be up and running. You will require these two libraries mongoose and mongodb


npm install express mongoose mongodb
yarn add express mongoose mongodb
import { connect } from "mongoose";
export const connectDB = () => {
const databaseUrl= "mongodb://localhost:27017" //Default URL for
DB running on localhost
connect(databaseUrl)
.then(()=>console.log('Database Connected..'))
.catch(error=>console.log(error.message))
}
dbConfig.js
import express from "express";
import { connectDB } from "./dbConfig.js";
const app = express();
const PORT = 8000;
connectDB();
app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log(`Server Started on
${PORT}...`);
});
node index.js
Database will be connected successfully!
MongoDB collections are highly scalable and easy to maintain as it supports dynamic schema and can be modified at any point without affecting any existing records, unlike SQL databases. Node.Js developers can easily perform CRUD operations using functional chaining and the response time is also less as compared to SQL databases.
MongoDB is a non-relational database and does not support concepts of Foreign Keys and Primary keys so relations cannot be established between different collections thus join query cannot be used to extract associated data, unlike SQL. But MongoDB has an aggregation framework that is strong enough to extract associated data and manipulate them.
Now Create a Book model and perform some CRUD operations on it.
import { model } from "mongoose";
const Book = model("books", {
name: { type: String, required: true },
description: { type: String, required: true }
});
export default Book;
import Book from "./bookModel.js";
const createData = async () => {
const data = new Book({
name: "The Great Gatsby",
author: "F. Scott Fitzgerald"
});
await data.save();
};
createData();
const getBooks = async () => {
const books = await Book.find({});
console.log(books);
};
getBooks();
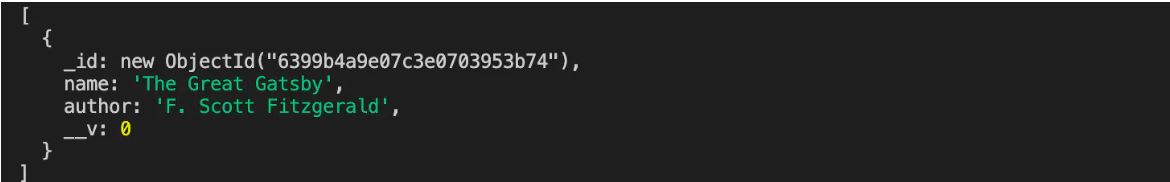
Now you will receive the data in the Books collection
Following these steps you can easily create and connect MongoDB databases to your application to your early-stage application.
TechTalk
15
People Speak
15

USA - Headquarters
Enterprise Minds Inc
12667 Alcosta Boulevard, Suite 410,
San Ramon, CA 94583
India - Hyderabad
4th Floor, Sy 41&42, Opp. Best Western
Jubilee Ridge, 17, Madhapur Rd, Kavuri Hills,
Hyderabad, Telangana 500033
Reach us at:
Post Resumes to:
© Enterprise Minds